Reaction Immune Complex Hypersensitivity. 1 Delayed hypersensitivity plays a crucial role in our bodys ability to fight various intracellular pathogens such as mycobacteria and fungi.
Type Iv Hypersensitivity Delayed Type Hypersensitivity Youtube
Though T cells are believed to orchestrate disease the type of T cell and the location and mechanism of T cell activation remain unknown.
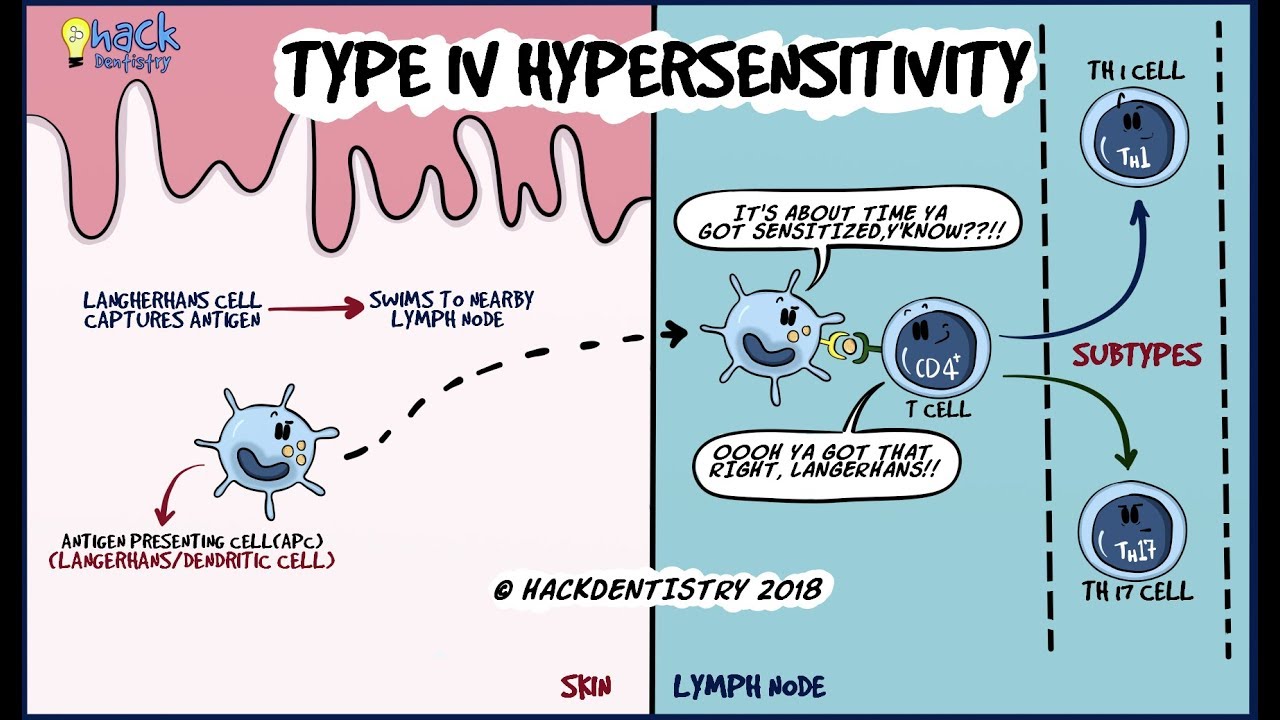
Types of delayed hypersensitivity reactions. This reaction is caused when CD4 Th1 helper T cells recognize foreign antigen in a complex with the MHC class II. Delayed hypersensitivity reaction. Blastomycosis and helminthic infections eg.
Edema of epidermis epidermal organic chemicals poison ivy heavy metals etc tuberculin 48-72 hr local induration lymphocytes monocytes macrophages intradermal. Delayed hypersensitivity reactions Type Reaction time Clinical appearance Histology Antigen and site Contact dermatitis 48-72 hr eczema lymphocytes followed by macrophages. They are distinguished from other hypersensitivity reactions by the lag time from exposure to the antigen until the response is evident 1 to 3 days.
Antibodies do not mediate DHR. DTH Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity response begins with an initial sensitization by antigen followed by a period of at least 1 to 2 weeks. Delayed hypersensitivity reaction also called type 4 hypersensitivity reaction or cell-mediated hypersensitivity reaction is inflammatory reaction initiated by T cells T-lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells that cause an inflammatory reaction to either exogenous or autoantigens which takes more than 12 hours.
Clinical care is negatively impacted by a limited understanding of disease pathogenesis. TH1 subtypes CD4 cells activate during the sensitization phase. Type IV hypersensitivity reactions Fig.
Delayed-type drug hypersensitivity reactions dtDHR are immune-mediated reactions with skin and visceral manifestations ranging from mild to severe. Typically the maximal reaction time occurs between 48 to 72 hours. A Type I hypersensitivity b Type II hypersensitivity c Type III hypersensitivity d Type IV hypersensitivity.
Mediated Hypersensitivity Allergy Hypersensitivity. Delayed hypersensitivity DH delayed type hypersensitivity DTH the type of hypersensitivity exemplified by the tuberculin reaction which as opposed to immediate hypersensitivity takes 12 to 48 hours to develop and which can be transferred by lymphocytes but not by serum. Which of the following hypersensitivity occurs via IgE antibody.
Type IV reactions are further subdivided into type IVa IVb IVc and IVd based on the type of T cell CD4 T-helper type 1 and type 2 cells involved and the cytokineschemokines produced. The most widely adopted current classification is that of Coombs and Gell that designates immunoglobulin-mediated immediate hypersensitivity reactions as types I II and III and lymphoid cell-mediated delayed-type hypersensitivitycell-mediated immunity as a type IV reaction. Hypersensitivity is sometimes also called allergy.
Contact hypersensitivity and. Delayed hypersensitivity can be induced by most viral infections many bacterial infections all mycotic. When some subpopulation of activated T helper cells encounters certain antigen they secrete cytokines that induce a localized inflammatory reaction called delayed type hypersensitivity DTH.
Hypersensitivity is of four types. Important diseases include tuberculosis leprosy listeriosis leishmaniasis deep fungal infections eg. It is mediated by T cells that cause an inflammatory reaction to either exogenous or autoantigens.
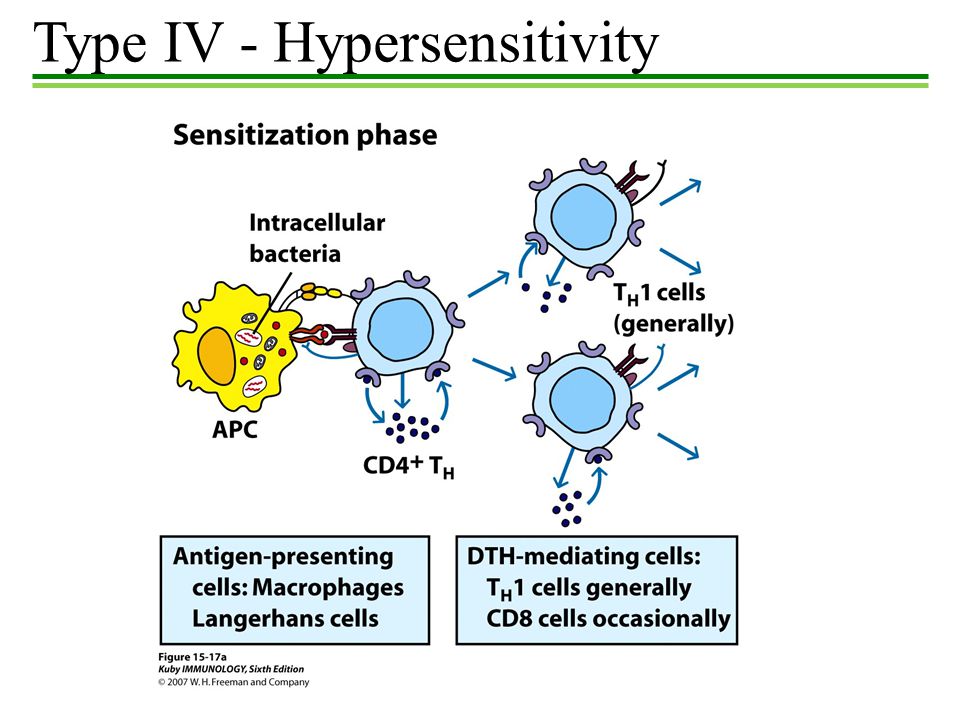
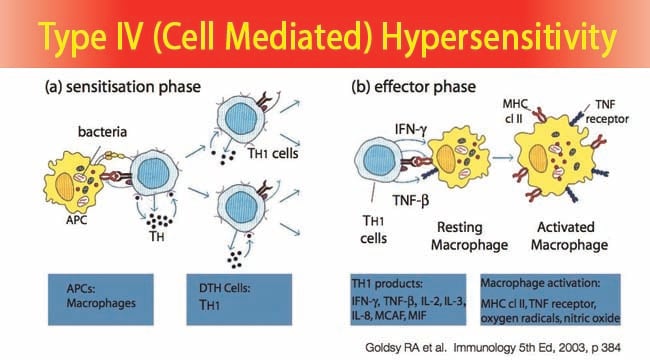
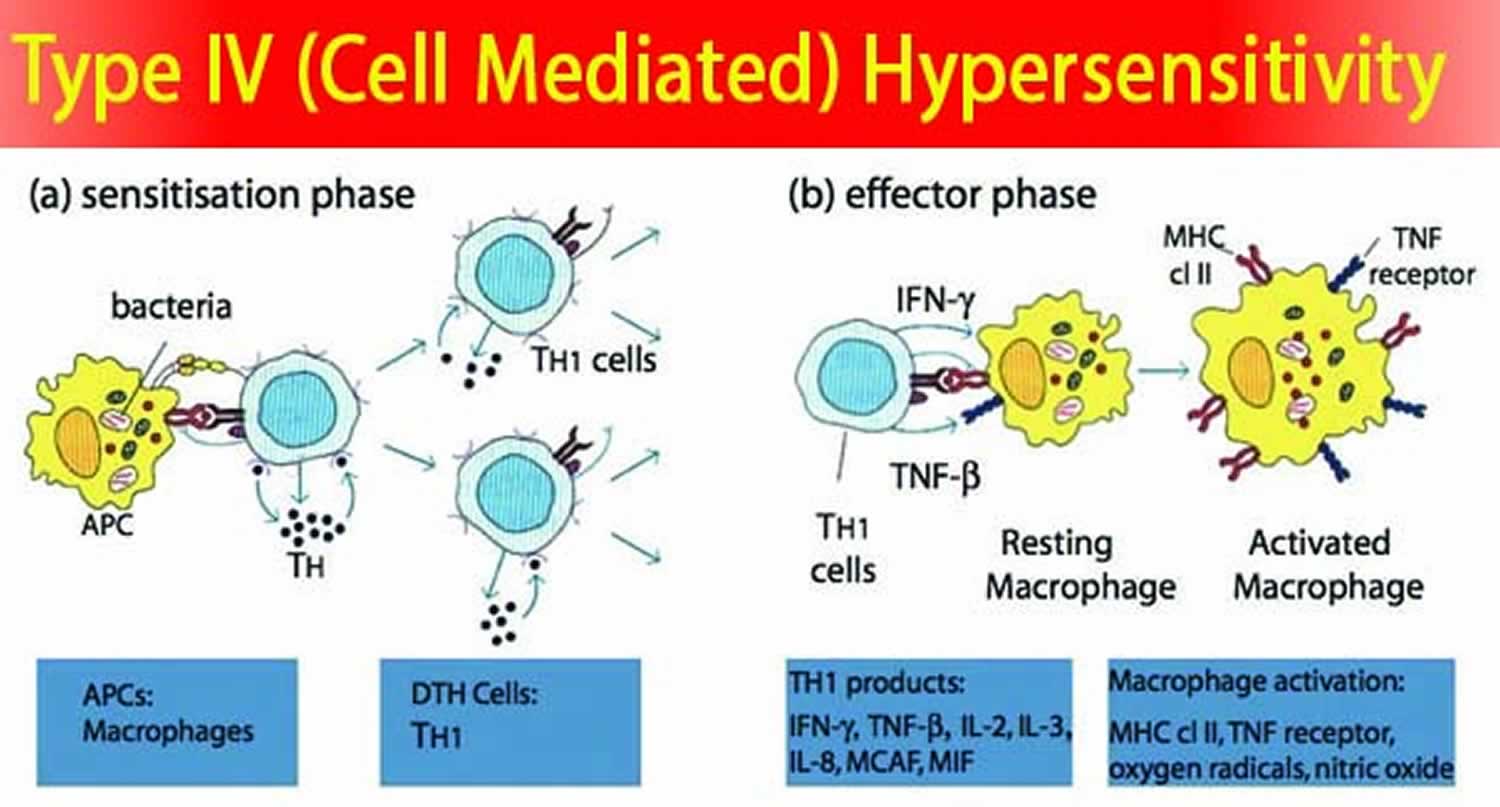
T-cells or macrophages are activated as a result of cytokine release leading to tissue damage. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction is also known as delayed type hypersensitivity DTH. 46-4 also known as delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions are mediated by antigen-specific effector T cells.
Type IV hypersensitivity is also known as delayed-type and involves of T-cell-mediated reactions. What is sterilization 2 types of sterilization 1. Delayed-type Hypersensitivity DTH T-cell-mediated Cytotoxicity.
T-cells or macrophages are activated as a result of cytokine release leading to tissue damage. The reaction is characterized by influxes of non-specific inflammatory cells particularly macrophages. Coombs and Gel classified type IV hypersensitivity reaction HR as a delayed hypersensitivity reaction DHR which takes more than 12 hours to develop.
DTH reactions are of two types. During this phase antigen-specific T cells activate and clonally expand. Type IV Hypersensitivity Reactions.
Delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions are a prominent feature of several chronic diseases in humans which for the most part are due to infectious agents such as mycobacteria protozoa and fungi. On Immediate and Delayed Hypersensitivity 1 Hypersensitivity reactions are broadly classified into four different types. Unlike the other types it is not antibody-mediated but rather is a type of cell-mediated response.
Type IV hypersensitivity is often called delayed type hypersensitivity as the reaction takes several days to develop. This response involves the interaction of T-cells monocytes and macrophages.

Type Iv Delayed Hypersensitivity Youtube

Type Iv Hypersensitivity Reaction Or Delayed Type Hypersensitivity Dth Online Biology Notes
Type Iv Cell Mediated Hypersensitivity Mechanism And Examples Microbe Notes

Type Iv Delayed Cell Mediated Hypersensitivity

Type Iv Hypersensitivity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Delayed Hypersensitivity Reaction Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment
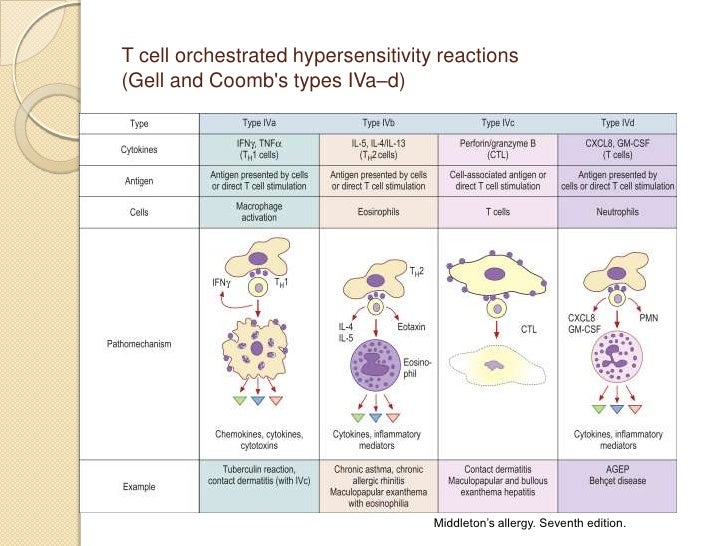
Delayed Type Drug Hypersensitivity
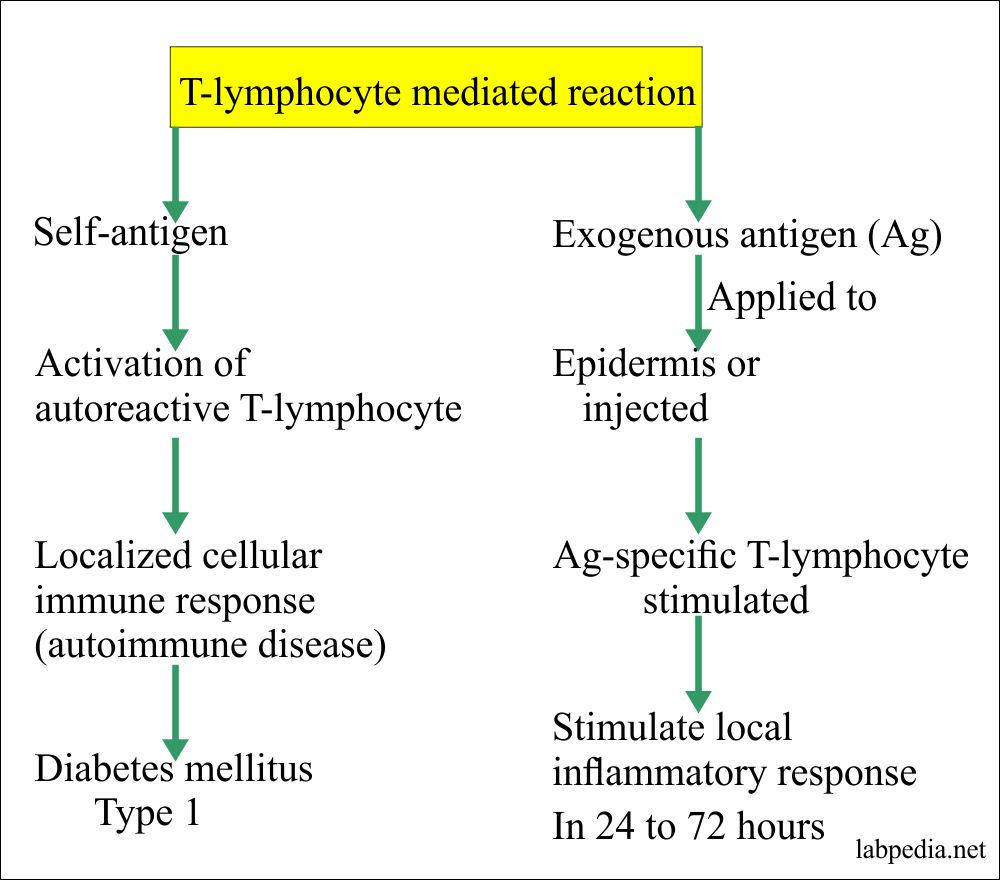
Chapter 14 Hypersensitivity Reaction Type Iv Cell Mediated Delayed Reaction Labpedia Net
